WordPress powers a large portion of the internet, which also makes it a frequent target for attackers. A single vulnerability can expose sensitive data or disrupt operations. Strong security practices reduce this risk and keep a site stable. At Arhpez Technologies, we work with businesses to build protected and reliable WordPress environments that can support ongoing growth. Hardened security begins with a structured approach that covers the server, the application, the user accounts, and the plugins that run in the system.
Use a Secure Hosting Environment
Security starts at the server level. A site becomes vulnerable if the hosting provider does not implement control measures such as isolated account environments, updated server software, web application firewalls, and frequent monitoring. We recommend hosting providers that support current versions of PHP, MySQL, or MariaDB, and hardened configurations. A strong server foundation prevents many common attacks before they reach the site.
Keep WordPress Core, Themes, and Plugins Updated
Outdated components are one of the leading entry points for attackers. WordPress core updates often patch discovered weaknesses. The same applies to plugins and themes. We encourage businesses to set a routine for checking updates. If the site uses custom code, new updates should be tested in a staging environment before deployment to avoid breaking functionality.
Limit Plugin Use and Audit Installed Extensions
Plugins add features but can introduce risk. Many attacks occur because of abandoned or poorly coded plugins. A periodic audit helps identify extensions that are no longer required or maintained by their developers. Removing unnecessary plugins reduces the attack surface and improves performance. Only plugins with strong update history, active support, and clean code practices should remain.
Configure Secure Authentication and User Permissions
Weak login credentials are a common vulnerability. We advise strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and user-access policies based on actual responsibilities. Administrators should not share accounts. Privileges should also be limited to the tasks each person needs. This protects the site if a single account becomes compromised.
Disable File Editing Inside the WordPress Dashboard
WordPress allows administrators to edit theme and plugin files through the dashboard. This feature is convenient but risky because attackers can insert malicious code through the same interface. The file editor should be disabled by adding a simple line to the wp-config.php file. Code changes should be handled in a development environment instead of the live site.
| define(‘DISALLOW_FILE_EDIT’, true); |
Use a Web Application Firewall
A Web Application Firewall filters traffic and blocks suspicious requests. WAF systems inspect patterns like SQL injections, cross-site scripting attempts, and brute force attacks. When combined with rate limiting, a WAF prevents many automated attacks that try to overload servers or test weak credentials.
Implement Database Hardening
Attackers often aim for the database because it contains valuable information. Changing the default WordPress table prefix adds a small layer of protection. Setting secure database authentication details and restricting user privileges in MySQL or MariaDB prevents unauthorized actions. Frequent database backups stored outside the public directory help with quick recovery during emergencies.
Use HTTPS and Strong SSL Configuration
An SSL certificate protects the connection between the user and the server. Sites still running on HTTP expose login credentials and other sensitive data. After installing an SSL certificate, the site should force all traffic through HTTPS. Security scans can verify if the SSL configuration uses modern protocols without weak cipher suites.
Enable Regular Backups and Offsite Storage
A hardened website still needs a reliable recovery plan. Backups should include files and databases. External storage prevents data loss if the primary server becomes inaccessible. Automated backup systems reduce human error. Versioned backups also help recover clean data if the site becomes infected.
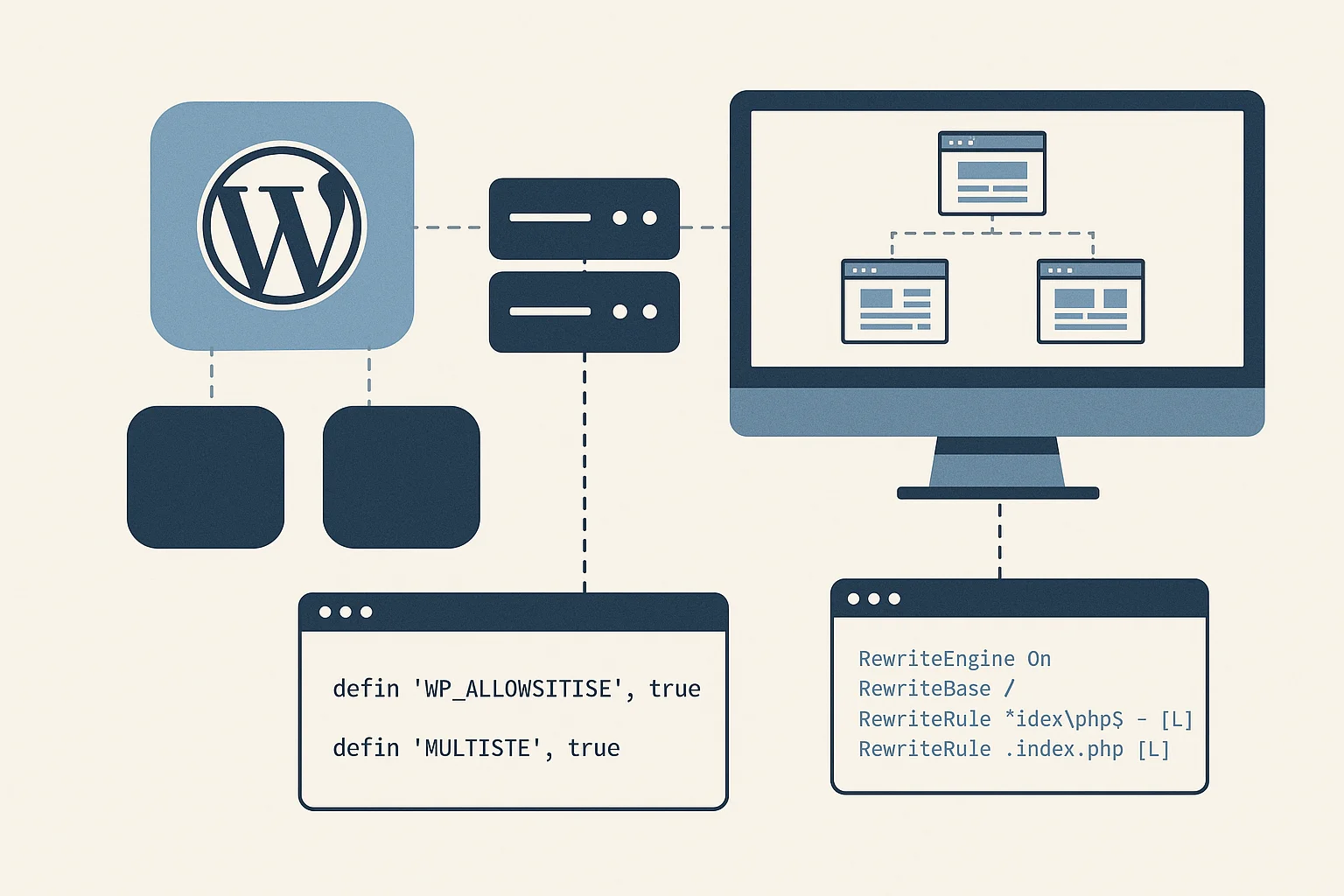
Protect wp-config.php and Sensitive Files
The wp-config.php file contains essential configuration values such as database credentials and authentication keys. Restricting access to this file through server rules adds strong protection. For Apache, this can be done through an .htaccess rule. Nginx users can apply a similar restriction inside the server block.
| <files wp-config.php> order allow,deny deny from all </files> |
Other sensitive directories like /wp-includes should also be restricted so that only necessary files can execute.
Limit XML-RPC Access
XML-RPC is a remote communication feature that attackers frequently test with brute force tools. Most sites do not require it. Disabling XML-RPC reduces unnecessary exposure. If a plugin depends on XML-RPC, rate limiting should be activated to restrict excessive login attempts.
Harden File Permissions
Incorrect file permissions allow attackers to upload malicious files or alter existing ones. WordPress recommends directories with 755 permissions and files with 644. These permissions balance security with functionality. Server-level ownership settings also matter because misconfigured ownership gives attackers the ability to modify core directories.
Monitor Activity and Logs
Security monitoring helps detect suspicious patterns early. Access logs and error logs show failed login attempts, unusual requests, or repeated hits to vulnerable endpoints. Activity log plugins can track admin actions like plugin installation or file changes. With proper monitoring, teams can respond before issues escalate.
Run Frequent Security Scans
Security scanners identify outdated components, file changes, malware signatures, and open vulnerabilities. We recommend running scans on a schedule. If malware is detected, the infected files must be cleaned and verified. After removal, the site should undergo a detailed review to confirm no hidden code remains.
Strengthen Security With Professional WordPress Development
Security is not a single feature. It is an ongoing framework. Businesses that rely on WordPress for operations need reliable development practices, secure configuration, and consistent monitoring. At Arhpez Technologies, we deliver secure setups and optimized workflows through our WordPress development services. Our focus on code quality, performance, and stable architecture helps protect projects from emerging threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I update plugins and themes on a WordPress site?
Updates should be checked weekly. High-risk updates such as security patches should be applied as soon as possible after testing in a staging environment.
What is the best way to protect a WordPress login page?
Use two-factor authentication, strong passwords, and rate limiting. A Web Application Firewall also blocks automated login attempts.
Do security plugins slow down WordPress?
Some plugins add overhead, but high-quality security tools use efficient scanning and caching techniques. A performance-optimized configuration avoids unnecessary load.
Is shared hosting safe for WordPress?
Shared hosting can be secure if the provider uses isolation methods and updated server software. Dedicated or virtual private environments offer stronger protection for high-traffic sites.
Should I disable XML-RPC on my WordPress site?
Yes, unless a required service depends on it. Disabling it reduces attack attempts that target authentication endpoints.
How often should backups be created?
Backup frequency depends on site activity. Active sites should run daily backups. Low activity sites can use weekly schedules. Offsite storage is essential for safe recovery.